The slaughter team zoomed in: the research on "artemisinin resistance" has made new breakthroughs
June 17, 2019 Source: Xinhua News Agency
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];Xinhua News Agency, Beijing, June 17 (Reporter Luo Guojun, Zhou Ning, Wang Junyi, Gai Boming) The team of the Tu Yu team put "big move"! In response to the "drug resistance" problem that artemisinin has appeared in some parts of the world in recent years, after years of hard work, Tu Yu and his team have made new breakthroughs in the "anti-malaria mechanism research", "the cause of drug resistance" and "adjustment of treatment methods". In the near future, it put forward a practical treatment plan to deal with the problem of "artemisinin resistance", and made new progress in the field of "artemisinin treatment of lupus erythematosus and other indications", "traditional Chinese medicine research and go out", and obtained the World Health Organization. Highly recognized by authoritative experts at home and abroad.
In-depth study of the anti-malarial mechanism to attack the "artemisinin resistance" problem
Artemisinin derivatives have been the most effective and uncomplicated combination of malaria since the discovery of artemisinin. However, the latest World Health Report on Malaria, published by the World Health Organization, shows that global malaria control has stalled and malaria remains one of the leading causes of death in the world. “The malaria infection rate and mortality rate will decline by 2020 by 40%. The phased goal of %" will be difficult to achieve. The reason is that in addition to the support for malaria prevention and treatment and the lack of coverage of core interventions, the resistance of malaria parasites to artemisinin-based antimalarial drugs is the biggest technical challenge facing global malaria.
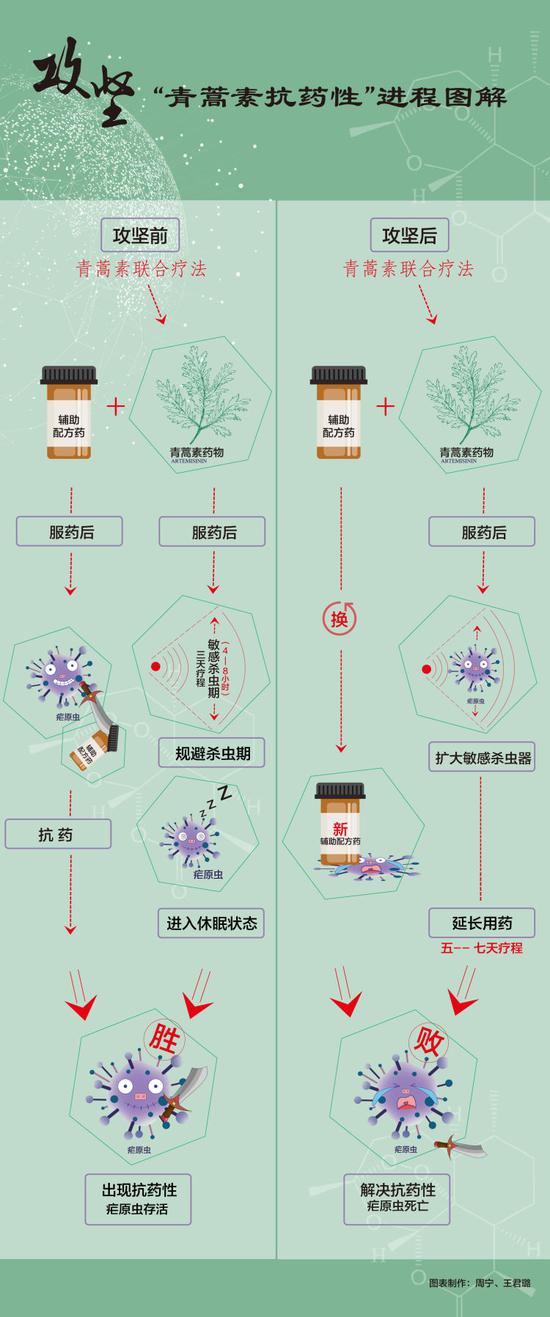
A number of studies by WHO and Southeast Asian countries have shown that artemisinin combination therapy ("artemisinin drugs" combined with "other antimalarial formulas" is used in malaria-infected countries in countries in the Greater Mekong Subregion, such as Cambodia, Thailand, Myanmar, and Vietnam. During the three-day cycle of treatment, the rate of clearance of the malaria parasite appears slowly and produces resistance to artemisinin.
"Artemisinin combination therapy is currently the first line of anti-malarial therapy promoted by WHO. It is the most important weapon against malaria in the world. Once the malaria parasite is generally resistant to it, the consequences will be very serious. Scientists all over the world are very worried. 'Artemisinin resistance' is further aggravated."
Tu Yu believes that in order to solve the problem of "artemisinin resistance", it is necessary to understand the mechanism of action of artemisinin. Wang Jigang, a member of the Tuyu team and a researcher at the Artemisinin Research Center of the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, said that the half-life of artemisinin in humans (the time required for the drug to decrease in vivo by half) is very short, only 1 to 2 hours, and is recommended for clinical use. The artemisinin combination therapy lasts for three days, and the truly effective insecticidal window of artemisinin is only limited to 4 to 8 hours. However, the existing drug-resistant strains fully utilize the short half-life characteristics of artemisinin to change the life cycle or temporarily enter a dormant state to avoid the sensitive insecticidal period. At the same time, Plasmodium can also produce significant resistance to the adjuvant anti-malarial formula in artemisinin combination therapy, which makes artemisinin combination therapy "fail".
After more than three years of research and development, the team has made new breakthroughs in the "anti-malaria mechanism research", "resistance of drug resistance" and "adjustment of treatment methods", and proposed a new treatment response plan: First, appropriate extension of medication time, by three Day therapy is increased to five or seven days of therapy; the second is to replace the adjuvant drug that has developed resistance in artemisinin combination therapy, and the curative effect is immediate.
The recent issue of the leading medical journal of the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) contains the major research results of the Tu Yu team and the “artemisinin resistance†treatment response program, which has drawn attention in the industry.
Tu Yu believes that solving the problem of "artemisinin resistance" is of great significance: First, it has strengthened the global research and development direction of artemisinin, that is, for a long time in the future, artemisinin is still the most effective drug for human antimalaria; Because of the low price of artemisinin antimalarials, each treatment only costs a few dollars, which is suitable for the poverty-stricken areas of Africa, which is concentrated in the affected areas, and is more conducive to achieving the goal of global malaria eradication.
"The global malaria prevention and control initiative is highly consistent with the Chinese government's initiative to build a community of human destiny." Pedro Alonso, director of the WHO Global Malaria Project, said, "As of now, artemisinin combination therapy cures malaria The number of patients has reached billions. The anti-malaria research work carried out by the team has been outstanding and the contribution is immeasurable."
Artemisinin in the treatment of lupus erythematosus: cautious optimistic results of the first phase clinical trial

The reporter learned that while the "artemisinin resistance" research has made new breakthroughs, the Tuyu team also found that dihydroartemisinin has a unique effect on the treatment of lupus erythematosus with high variability.
Zhang Boli, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and former dean of the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, said that traditional treatment of lupus erythematosus can only be treated conservatively with immunological agents, which is difficult to cure and has secondary infections.
According to the previous clinical observation of the Tuyu team, the efficacy of artemisinin in the treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus was over 90% and 80%, respectively. Pedro Alonso affirmed this possibility, and he also believes that further thorough clinical trials and rigorous clinical trials must be based on international standards to reach a final conclusion.
The State Drug Administration's "Drug Clinical Trial Approval" shows that the "dihydroartemisinin tablets for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus and discoid systemic lupus erythematosus" submitted by the Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences The Clinical Trial application has been approved. Kunming Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. is the responsible unit to carry out clinical trials.
Xue Qiao, medical manager of Kunming Pharmaceutical Group, said that under the guidance of the team, the first phase of the clinical trial was officially launched in May 2018. The design samples were 120, from Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking University First Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical University. Affiliated hospitals, the People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University and other 15 leading units nationwide participated in the joint venture.
"Approximately 500 Chinese and foreign patients enrolled in the clinical trial were rigorously screened through multiple processes such as 'disease activity score', and the first batch of volunteer patients have been enrolled in the trial." Xue Qiao said, "From the current situation, volunteer patients do not have Unexpected adverse events occurred."
Tu Yu said: "Artemisinin has a tendency to treat lupus erythematosus, and we are cautiously optimistic about the success of the trial."
The reporter learned that clinical trials generally have three phases, and the second and third trials have a larger sample size, at least 7 to 8 years. If the test is successful, it is expected that the new dihydroartemisinin tablets will be approved for marketing as early as 2026.
Traditional Chinese medicine research such as artemisinin is expected to be included in the Oxford Medical Textbook for the first time.
The reporter learned from the Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences that the traditional Chinese medicine research, such as artemisinin, written by experts from the Tuyu team and researcher Liao Fulong of the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, is expected to be included for the first time in the forthcoming international authoritative medical textbook "Oxford Medical Textbook (Sixth Edition). )". The industry believes that this will become an important practical result of the "going out" of Chinese medicine culture.
According to Liao Fulong, the chapter entitled “The Model of Traditional Medicine——Chinese Medicine†has been finalized and divided into “What is Traditional Medicineâ€, “History of Artemisinin and Other Chinese Medicines, Mechanism of Action and Clinical Application†And the syndrome differentiation and treatment and "traditional medicine can be easily accessible" four major parts. In April of this year, the publisher of the book, Oxford University Press, has initiated proofreading work and will be reprinted in the second half of this year.
Professor Cox, editor-in-chief of the Oxford Medical Textbook, said that he was pleased with the traditional Chinese medicine to be included in the textbook. He said: "The Chinese medicine chapter is both important and profound. All this is the result of the outstanding efforts of Chinese scientists."
Authoritative experts such as Pedro Alonso believe that the team has paved the way between traditional medicine and modern medicine, making Chinese medicine not only widely used in China, but also recognized by more and more countries for effective treatment. It is hoped that Chinese scientists will continue to make more voices on the international stage of artemisinin research.
Electronics Industrial Nitrile Gloves
Electronics Industrial Nitrile Gloves,Pure Nitrile Exam Gloves,Waterproof Gloves For Work,Astm D6978 Examination Gloves
Puyang Linshi Medical Supplies Co., Ltd. , https://www.linshimedicals.com