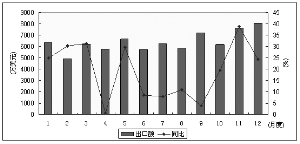
Business News March 21st Customs statistics show that in 2010 China's import and export trade of Chinese medicines continued to maintain steady growth, of which the total amount of import and export of plant extracts reached 950 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 16.1% year-on-year, accounting for 35.9% of the total import and export volume of Chinese medicines. The total amount of imports and exports was basically flat with an increase of 0.36%. Exports of plant extracts amounted to US$820 million, an increase of 17.6% year-on-year, accounting for 41.9% of China's merchandise merchandise exports; exports amounted to 46,000 tons, an increase of 3.2% year-on-year; average export prices rose slightly, up 14.0% year-on-year. Imports amounted to 130 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 7.2% year-on-year, accounting for 18.8% of the import volume of Chinese medicines; import volume was 1 million tons, a year-on-year decrease of 10.4%; average import prices increased by 19.6% year-on-year. It is worth noting that in 2010, the European Union's extract market soared across the board, and China's export of plant extracts to the EU increased in volume and price.
European market recovers From the perspective of export regions, the export volume of China's plant extracts to major target markets has increased significantly in 2010. From the analysis of customs data, this increase mainly comes from the increase in average export prices. In addition to the European and Asian markets, the number of exports has declined to varying degrees in other markets. Overall, Asia, Europe, and North America are still the main regions for the export of plant extracts in China. The export volume of these three regions accounted for 88.2% of the total export volume of China's plant extracts. In 2010, the export volume of China's plant extracts to the EU market was US$180 million, an increase of 49.2% year-on-year; the number of exports increased by 15.8% year-on-year; the average export price increased by 28.8% year-on-year. It can be seen that European countries have basically recovered from the impact of the financial crisis in 2009, and the market has grown significantly.
In 2010, the export volume of China's plant extracts to Asia was US$400 million, an increase of 12.4% year-on-year, accounting for 49.6% of the total export volume of plant extracts. Among them, the ASEAN market has made a huge contribution. In 2010, China's exports to the ASEAN market reached 130 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 35.1% year-on-year. The formation of the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area has played a positive role in promoting the development of the Asian plant extract market, and has also made it very likely that the ASEAN region will become a new sustainable growth point for extracts exports in the future.
Traditional market performance is flat
The top five markets for China's export of plant extracts in 2010 were Japan, the United States, Malaysia, India and Mexico. Overall, these traditional markets performed flat and the steady increase in exports was due to the increase in average export prices. Specifically, China’s export of plant extracts to Japan was US$140 million, an increase of 6.9% year-on-year; the number of exports increased by 8.5% year-on-year, and the average export price declined slightly. China's export of plant extracts to the United States amounted to 120 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 5.4% year-on-year, and the number of exports decreased by 7.4%. The reason, I believe that there is a certain relationship with the full implementation of the United States dietary supplement cGMP. According to the FDA regulations, all manufacturers of dietary supplements in the United States must comply with c GMP regulations in June 2010 at the latest. As a major source of raw materials for U.S. dietary supplements, China's export of plant extracts has also been subject to stringent quality requirements. At present, most companies have a smooth transition, and their quality has also been improved to some extent. In 2010, the market for plant extracts in most European countries performed well, and exports to these countries increased in volume and price. However, the performance of the Korean market in Mexico, Spain, and Asia was not satisfactory, and the number of exports declined significantly. The specific reason is unknown, and its market changes still need further observation.
Industrial competitiveness needs to be improved
In 2010, the export volume and export volume of plant extracts in most provinces in China maintained a steady increase. Among them, Shandong, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Guangdong ranked the top four in terms of export value, with a total export value of US$ 330 million, accounting for 40.4% of China's total export volume of plant extracts. There are 656 plant extract export enterprises in these four provinces and cities, accounting for 51.3% of the total number of exporters of plant extracts in China (1279) in 2010, reflecting that the export enterprises of plant extracts in China have certain geographical agglomeration characteristics. However, from the data of industry concentration (CR8, the ratio of exports of the top eight companies in exports to the total export volume of China's plant extracts), it still belongs to a low concentration of competitive industries, indicating the level of industrial concentration of plant extracts. Relatively low, international competitiveness still needs to be improved.
From the perspective of corporate structure, there were 1279 enterprises engaged in extracts exports in 2010, an increase of 8.6% year-on-year. Among them, 48.1%, 36.4%, and 15.2% of the export value of private enterprises (925), "funded enterprises" (164), and state-owned enterprises (185) are respectively accounted for. On the whole, the scale of China's plant extracts export enterprises is still generally small, and foreign participation is relatively high.
From the perspective of export varieties, in 2010, the export volume of individual plant extracts in China showed a steady growth in general. Among them, the export value of extracts under the comprehensive code “Unlisted Vegetable Juices and Extracts†and “Other glycosides and their salts, ethers, esters, and other derivatives†were 350 million and 190 million U.S. dollars, respectively. Among the key varieties, the exports of “Licorice Juice Extract†and “Rutin and its Derivatives†were US$19.743 million (an increase of 2.5% year-on-year) and US$15.792 million (a year-on-year increase of 44.9%), which were stable.
On the whole, the export trade of plant extracts in China was stable in 2010, and most markets maintained stable growth. However, compared with previous years, the main traditional market for plant extracts has shown signs of slowdown. In recent years, mainstream markets such as Europe, the United States, and Japan have become more localized in variety selection, and have put forward new requirements for product prices and safety. In response to the new changes in the international market, some domestic companies with keen sense of smell have begun to make strategic adjustments. Therefore, to remind domestic plant extracts enterprises, according to their own industrial characteristics, actively through the industrial chain extension and new product development and other ways to promote the improvement of the company's international competitiveness.
Hebei Orient Imp. & Exp. Co. Ltd. , https://www.orientmedcare.com
 Business News March 21st Customs statistics show that in 2010 China's import and export trade of Chinese medicines continued to maintain steady growth, of which the total amount of import and export of plant extracts reached 950 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 16.1% year-on-year, accounting for 35.9% of the total import and export volume of Chinese medicines. The total amount of imports and exports was basically flat with an increase of 0.36%. Exports of plant extracts amounted to US$820 million, an increase of 17.6% year-on-year, accounting for 41.9% of China's merchandise merchandise exports; exports amounted to 46,000 tons, an increase of 3.2% year-on-year; average export prices rose slightly, up 14.0% year-on-year. Imports amounted to 130 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 7.2% year-on-year, accounting for 18.8% of the import volume of Chinese medicines; import volume was 1 million tons, a year-on-year decrease of 10.4%; average import prices increased by 19.6% year-on-year. It is worth noting that in 2010, the European Union's extract market soared across the board, and China's export of plant extracts to the EU increased in volume and price.
Business News March 21st Customs statistics show that in 2010 China's import and export trade of Chinese medicines continued to maintain steady growth, of which the total amount of import and export of plant extracts reached 950 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 16.1% year-on-year, accounting for 35.9% of the total import and export volume of Chinese medicines. The total amount of imports and exports was basically flat with an increase of 0.36%. Exports of plant extracts amounted to US$820 million, an increase of 17.6% year-on-year, accounting for 41.9% of China's merchandise merchandise exports; exports amounted to 46,000 tons, an increase of 3.2% year-on-year; average export prices rose slightly, up 14.0% year-on-year. Imports amounted to 130 million U.S. dollars, an increase of 7.2% year-on-year, accounting for 18.8% of the import volume of Chinese medicines; import volume was 1 million tons, a year-on-year decrease of 10.4%; average import prices increased by 19.6% year-on-year. It is worth noting that in 2010, the European Union's extract market soared across the board, and China's export of plant extracts to the EU increased in volume and price.