Release date: 2016-11-30

Recently, in a research report published in the international journal Scientific Reports, researchers from Imperial College London have developed a new detection technology for HIV . The researchers said that they have developed a test in a USB flash drive. A new device for HIV that uses a drop of blood to detect the presence of HIV. Researchers then use computers and handheld devices to read electrical signals generated by the device. This one-time test can be used to monitor HIV patients. The state of disease treatment.
In this article, Xiaobian has taken stock of the development of new technologies in the field of HIV testing in recent years, and learn with you!
[1]Science: Imaging technology to monitor the spread of HIV in vivo
Retroviruses (such as HIV) in the host how to spread, scientists have not known, recently, researchers from Yale University through research and design a way to achieve observation of HIV diffusion processes in living organisms The related research was published in the international journal Science, in which the researchers successfully observed how HIV reaches and spreads in the lymph nodes of mice.
Researcher Walther Mothes said that the way we observed the spread of the virus is not the same as people imagined. In the experiment, we tracked the fluorescently labeled virus in the mouse body and used complex imaging techniques to capture the combination of viral particles. The process of phagocytosis, which is accomplished by viscous proteins located on the surface of the lymph nodes.
The researchers said that the captured virus particles can be opened to a rare type of B cell, and then the virus particles will adsorb themselves to the tail of these B cells and be dragged into the lymph nodes. These B cells will be the same within one to two days. The organization establishes a stable connection to promote the complete transmission of the virus.
The video taken by the researchers describes a potential way to help suppress the tissues surrounding the HIV-infected area. If researchers can develop a way to block HIV's use of sticky proteins to bind macrophages, then the virus Diffusion propagation is suppressed.
[2] Heavy! Scientists develop the world's first next-generation sequencing technology to measure HIV drug tolerance mutations
At the AACC Annual Meeting and Clinical Lab Expo, researchers from Singapore's genetic sequencing company, Vela Diagnostics, launched the world's first HIV drug resistance mutation. A new generation of sequencing technology that plays an important role in helping clinicians optimize HIV treatment systems , while also helping scientists to take the initiative to minimize the global antiretroviral drug tolerant epidemic.
The use of antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection has grown dramatically over the past decade and is also part of the current global adoption of the AIDS public health threat program; according to data from the World Health Organization, HIV drug tolerance Concurrent growth will counteract the efforts of scientists over the years by offsetting the effects of antiretroviral drugs on HIV and AIDS progression; therefore, testing patients' tolerance to HIV drugs is key to ensuring effective treatment for patients. At the same time, it is also very important to effectively manage the tolerance of antiretroviral drugs.
[3]Analy Chem: A new mobile DNA detection technology for monitoring HIV
Recently, in a research report published in the international magazine Analytical Chemistry, scientists from Rice University in the United States have developed a simple and high-accuracy detection technology to detect the signs of HIV and the degree of disease development in patients' bodies.
Researcher Rebecca Richards-Kortum said that the current gold standard for diagnosing HIV status in infants relies on laboratory equipment and currently available detection techniques to monitor viral load in their bodies, and researchers in this paper have developed A new nucleic acid-based HIV detection technology.
The new detection technology is based on a PCR-based method for amplification of recombinant polymerases (RPA), which replaces complex laboratory testing steps that allow rapid multi-amplification of genetic markers in the blood, resulting in genetic markers of the virus. The object can be easily detected; qRPA detection can be used to perform targeted labeling of fluorescent probes on specific sequences in HIV DNA, thereby using a machine for quantitative detection, and finally by software analysis of fluorescent DNA, doctors can master Dynamic information about HIV in the patient's body.
[4] Brushing saliva for 15 minutes to test AIDS at home
The most common method of AIDS testing is to use the kit to detect and pump blood tests. Kit testing typically requires 50 or more people to work together, and the results typically take several days. The rapid blood test can get the test results within 30 minutes, but it requires professional doctors to operate around. So, is there a simpler and more practical detection method?
In the Science and Technology Incubation Park of Suzhou High-tech Zone, Suzhou Wanmuchun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. revealed that they independently developed the first integrated HIV saliva detector in China and successfully obtained the highest level of production license for the national medical device. “ Efficient, it can be read in 10 to 15 minutes; it is convenient to brush saliva; to protect privacy, patients can self-test at home. â€
The company's R&D personnel took out a small test stick from the box and showed it to the reporter. As long as the tooth was pulled out of the entrance cavity and the test stick was taken out from the mouth for a while, the “display window†will show colored lines, and the test results will be clear at a glance.
Cheng Hong, general manager of the company, told the reporter that the AIDS saliva rapid detector is the first to use nano-polymer porous material as a sample collection and transmission unit. By collecting the oral fluid of the examinee and analyzing whether it carries a certain pathogen through immunoassay. Achieve similar effects to blood tests. At present, this "one-piece HIV saliva detector" has been authorized by the national invention patent.
[5] British scientists have developed a cheap and cheap HIV test method
Scientists at Imperial College of Science and Technology have developed a new HIV test that is 10 times more sensitive than current tests, but at a relatively low cost, which is a diagnosis for HIV-infected people in developing countries. Treatment brings a new gospel.
At present, the use of human saliva to detect HIV has been quite simple and fast, but its disadvantage is that it can only be detected when the viral load reaches a certain concentration. In some cases, the viral load of the test sample is too low, and it is difficult to obtain accurate results using some of the original detection methods (such as saliva detection), and a "false negative" test result usually occurs. The new method can accurately detect the situation where the viral load is too low.
The new detection method uses nanotechnology, which can display the test result of the sample to be tested as red or blue, which can be distinguished by ordinary naked eyes. The method is to test the serum and detect in the disposable vessel whether there is an HIV biomarker called p24.
If p24 is present (even at very low concentrations), it will cause tiny gold nanoparticles to condense together in an irregular manner, which in turn causes the solution to turn blue; a negative result can separate the gold nanoparticles into a spherical shape. The solution is shown in red.
[6] American scientists developed molecular microscopy for in situ detection of HIV
The HIV in situ analysis technology has once again made a breakthrough. At the International AIDS Conference held last week, American scientists demonstrated their new detection technology and test results. This probe called "Molecular Microscope" can accurately detect the hidden places of HIV inside and outside the cell.
Ricardo Pul, deputy director of the Vaccine Research Center of the American Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said that the new technology of this molecular microscope is magical, and its super powers can fully understand the traces of HIV in any cell. Help clear the mystery of the long-term survival of HIV, so that it can be completely removed from the body.
New technology is almost undisturbed
The in situ analysis techniques used to detect HIV in tissues currently face common problems. These detection techniques, whether using fluorescent substances as markers or radioactive materials for labeling, are often difficult to accurately locate the location of HIV in tissue samples, and it is often difficult to separate surrounding cellular material with target analytes, such as HIV RNA and DNA. The difference is open.
These markers misidentify the cell tissue as a virus and cause background interference in the analysis of the results.
[7] DNA nanometer "machine" that can quickly detect viruses
A nanoscale machine made of synthetic DNA can diagnose many diseases including AIDS quickly, accurately and inexpensively.
Recently, a study may revolutionize the lengthy, cumbersome, and expensive antibody testing process to help doctors better diagnose infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and HIV. An international research team designed and synthesized a nanoscale DNA "machine" with custom modifications that allowed them to identify specific target antibodies. This month, the new method was published in the Journal of Applied Chemistry (Angewandte Chemie), and the research team promised to continue to develop fast, inexpensive bedside antibody detection technology. This technology helps us to detect the disease early and save medical costs.
When an antibody binds to DNA, the structure changes or transforms, which in turn produces an optical signal. The sensor not only does not require chemical activation, but also responds within five minutes. These features allow us to easily detect target antibodies even in the face of complex clinical samples such as serum.
[8] Sci Rep: Innovation! Scientists have developed a new device that can quickly detect HIV infection using a USB stick!
A recent study published in the International Journal of Scientific Reports, researchers from Imperial College London have developed a new device for detecting HIV in a USB flash drive that can be detected with a single drop of blood. The existence of HIV, and then the researchers used computers and handheld devices to read the electrical signals generated by the device. This one-time detection method can be used to monitor the condition of HIV patients.
In addition, the technology can help HIV patients in remote areas to manage the disease effectively. The new equipment developed by the researchers is not only very accurate, but also can produce results within 30 minutes ; it can monitor the amount of HIV in the blood, which It is essential to reflect the patient's treatment indirectly.
Current methods of routinely carrying out viral load in HIV patients often take several days, sometimes even longer, including the time from transporting a patient's blood sample to the laboratory, in many parts of the world. Especially in areas with high HIV-infected areas, routine testing methods are simply unable to meet the disease monitoring needs of everyday patients.

[9] Ultra-sensitive sensors help doctors detect HIV and prostate cancer with the naked eye
Recently, scientists have developed an ultra-sensitive sensor that allows doctors to detect diseases and viruses with the naked eye . The study was published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Research teams from Imperial College London report that their vision sensor technology is 10 times more sensitive than current methods for measuring biomarkers. This technology can be used to detect HIV and prostate cancer. Researchers say their sensors will help to detect and treat patients cheaper and easier.
In this study, the sensor designed by the research team detected HIV infection in patients by detecting the biomarker p24 in blood samples. Professor Molly Stevens of the School of Materials and Bioengineering, Imperial College, London, UK: It is important that the technology enables patients to be regularly tested to assess the success of retroviral therapy and to check for new infections.
The technology has higher sensitivity, does not require complicated instruments, and is ten times cheaper, allowing for better screening of multiple diseases. The researchers also tested the prostate-specific biomarker PSA and the results were fairly sensitive and accurate.
The team also reported that the sensor is very sensitive and can be detected when the patient's viral load is low, while routine tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are not very sensitive.
[10] The world's first home-based AIDS testing equipment OraQuick was approved for listing
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the launch of an HIV detector on the 3rd of this month. The HIV detector is a household.
Ora Quick Test (OraQuick) is an oral detector previously introduced by American biotechnology company Olahuer Technology. The user holds a special medical sponge to slide between the upper teeth and the gums and between the lower teeth and the gums to collect biological samples. The user then inserts the sponge into a small test instrument and waits 20 to 40 minutes to know if he is infected with HIV .
According to the latest data from the US government, about 1.2 million people in the United States are HIV-positive, but 20% of patients are unclear about the condition. The Food and Drug Administration said that with this equipment, patients can monitor their condition anytime and anywhere. There is no need to go to the hospital, and some civil society groups that advocate the promotion of HIV prevention knowledge believe that this detector can protect people's privacy while protecting people's situation.
According to the company, according to the results of the approval of the Food and Drug Administration, consumers are expected to buy the detector at the retailer's counter in October this year, and they will know if they are infected with HIV for up to 40 minutes.
At the same time, consumers can also purchase through the Internet. There are more than 30,000 drug dealers and homeware stores in the United States.
Source: Bio Valley
Glow In Dark Tape
1. Material and classification of glow in dark tape
We have PET material glow in dark tape and PVC material glow in dark tape. PET material is cheaper but not printable. PVC material support customized printing with low MOQ.
For both materials, we have different kinds according to the glowing time it can last after full charging (0.5hours charging at least). We have 2hours, 4hour, 6hours, 8hours and 10hours according to the glowing period it can last.
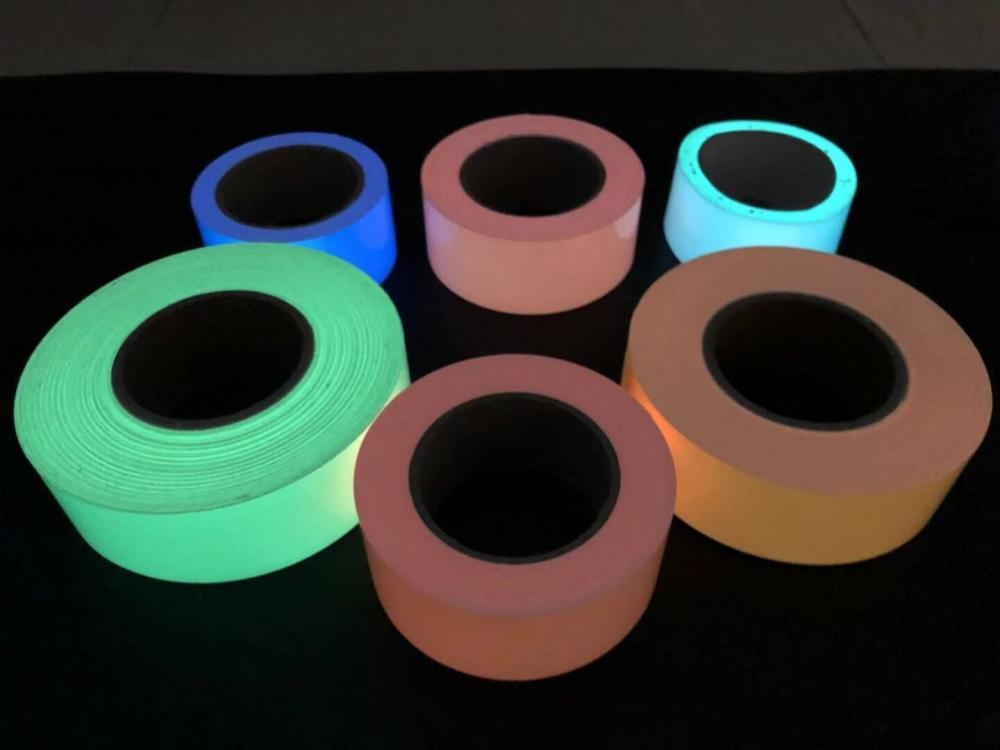
2. Colors for choosing
We have light green, pink, orange, red, blue, white for choosing.
3. Features
a. Good ahesion, we use solvent acrylic adhesive, the adhesive is strong and long lasting.
b. Waterproof. Both PET and PVC material are waterproof. Can used for both indoor and outdoor usage.
c. Long service life: 2~3 years even for outdoor usage.
d. Different sizes for choosing: 1.24m x 45.7m log roll, or other customized sizes such as 25mm/ 50mm x 5meters/ 10yards/ 10meters/ 18meters, etc.
e, Accept die cuting to small pieces such as dots, stars, arrows, etc,
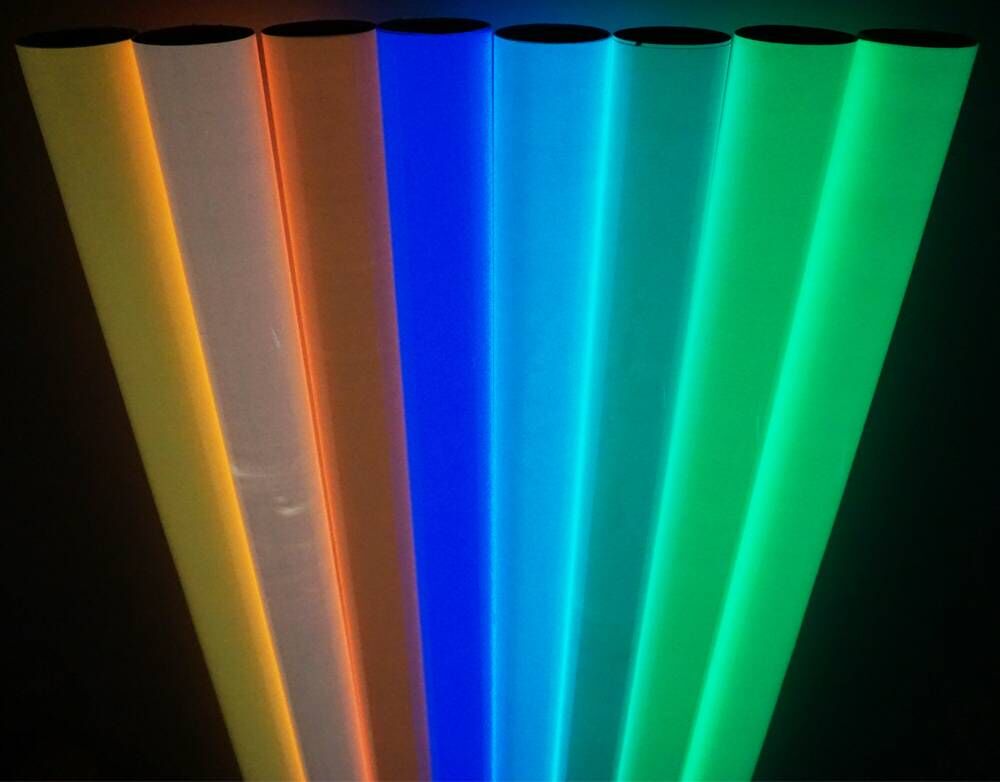
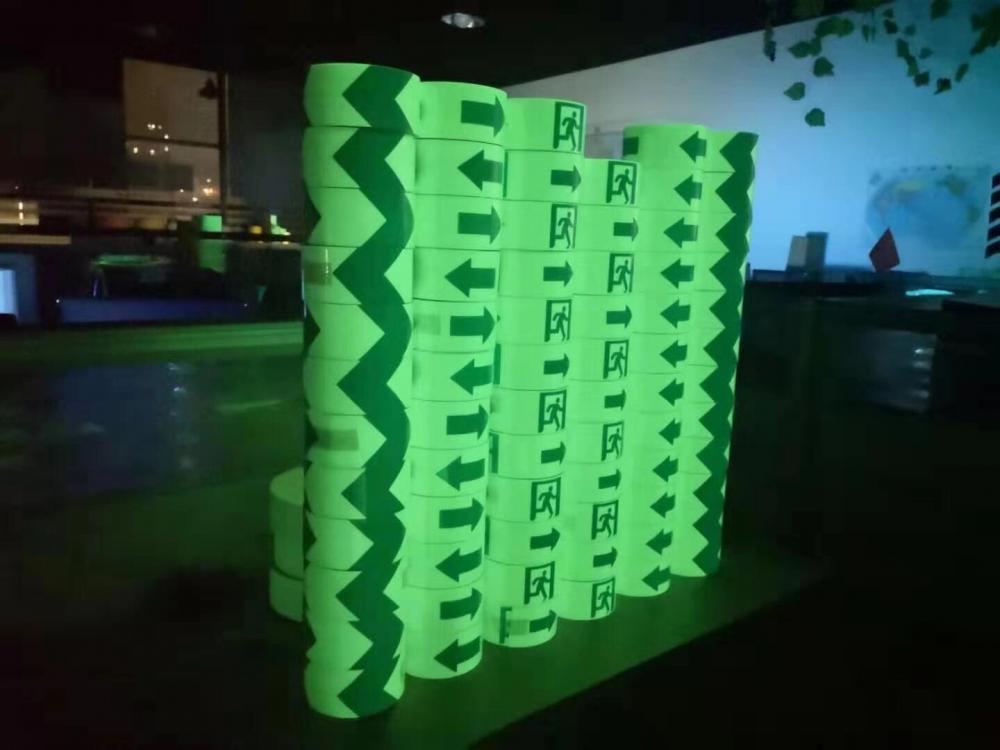
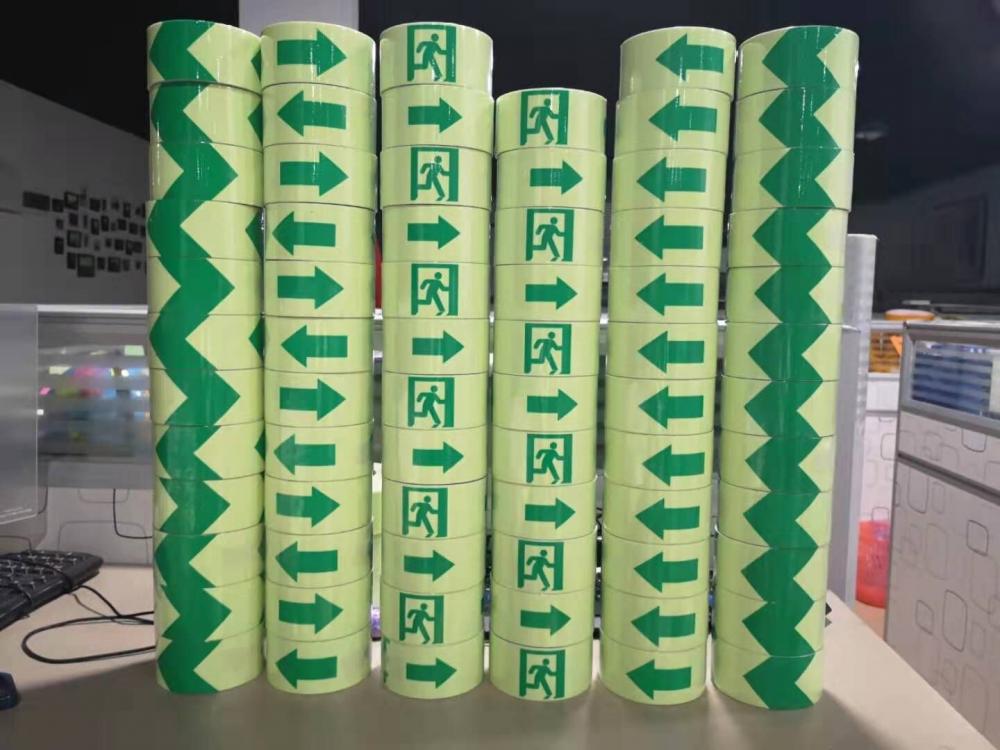
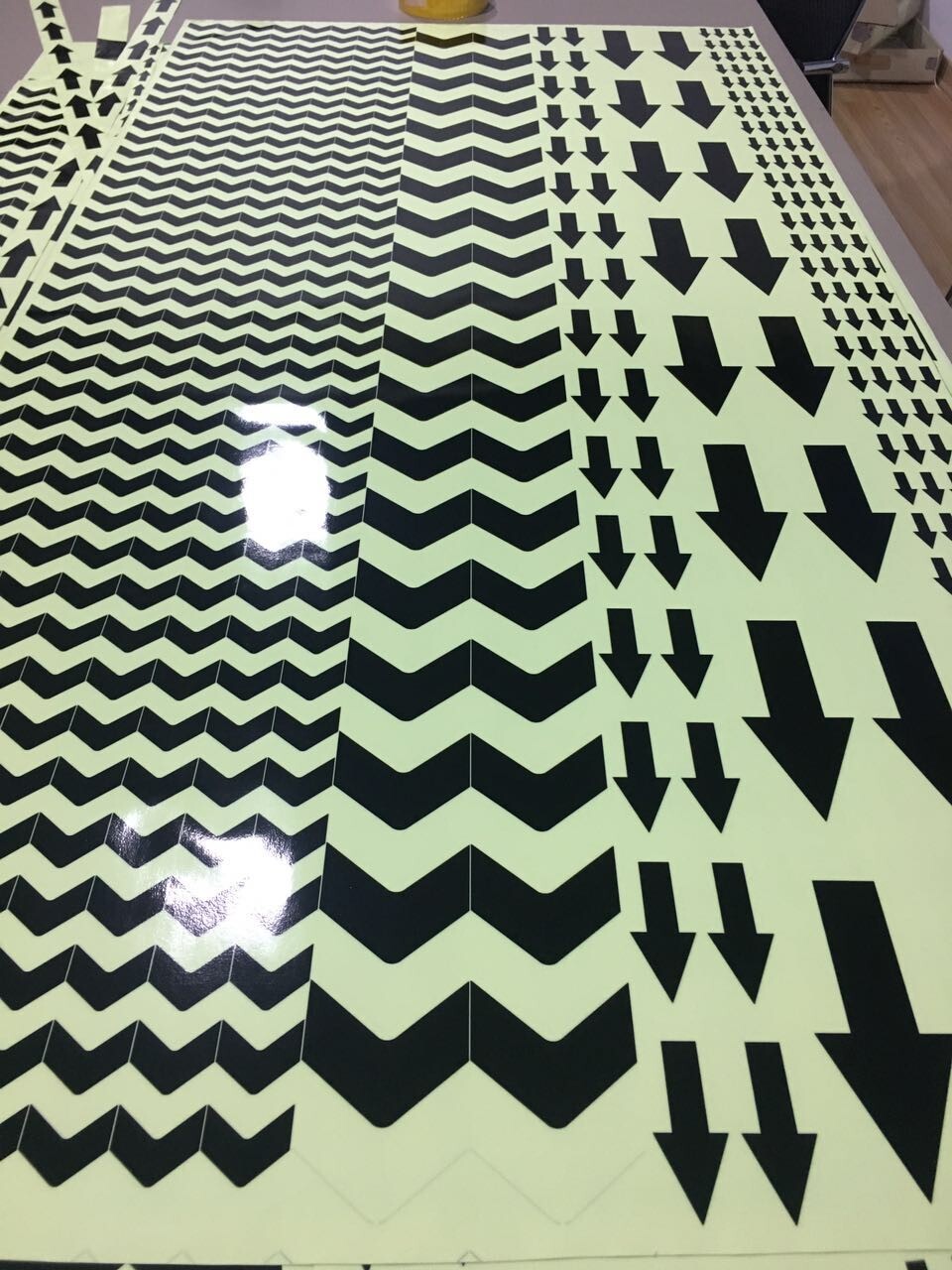







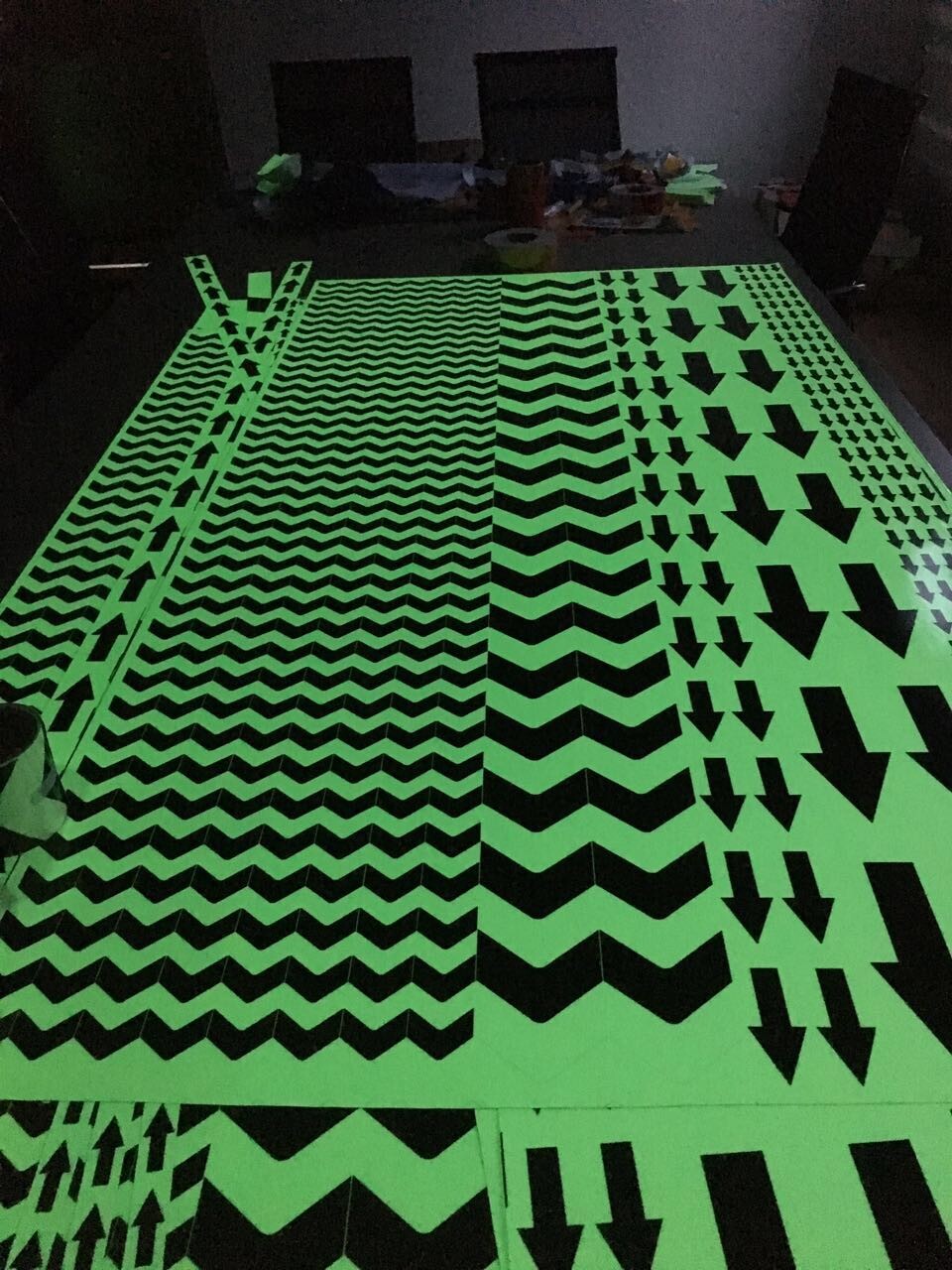
Glow Grip Tape,Luminous Adhesive Tape,Waterproof Glow In The Dark Tape,Glow In The Dark Reflective Tape
Kunshan Jieyudeng Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jerrytape.com