Dr. Jody Mason JBC article published in the United States to verify the method of constructing an anti-α- S yn peptide aggregation inhibitor, and a peptide sequence as a promising potential drug candidate molecules. Dr. Mason commented: " Using CEM's Liberty Blue for peptide synthesis experiments , it can quickly synthesize the peptides needed for research, saving us a lot of cost and time. We are willing to try more research and face more. Risks and challenges. Liberty Blue is a great addition to our lab and I highly recommend other researchers to use it."
Parkinson's disease is a progressive disease of the nervous system, accounting for about 15% of all dementia. More common in the elderly, according to the statistics of domestic authorities, the prevalence rate of people over 65 years old in China is about 1.7%, and it increases with age. According to calculations, the number of patients with Parkinson's disease in China has exceeded 2.2 million.
The current medical level is still unclear about the exact cause of this pathological change, and there is no clear diagnosis method (mainly relying on medical history, clinical symptoms and signs). At present, drug treatment is the most important treatment, and surgical treatment is medical treatment. An effective supplement. Although the applied treatment can not prevent the progression of the disease, it can not cure the disease, but it can improve the symptoms and effectively improve the quality of life of patients.
For this "difficult situation", major pharmaceutical companies have tried their best. In recent years, several new Parkinson's drugs have been listed, such as Opicapone, GOCOVRI (sustained release amantadine), etc. In the case of progressive disease, it has not yet broken through the previous target. Due to the difficulty of research and development and financial pressure, Pfizer, the world's largest pharmaceutical company, announced in early 2018 that it would abandon the development of new drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, and abolish about 300 relevant positions in time science research and early development projects. The difficulty in developing Parkinson's drugs can be seen.

The pathological feature of Parkinson's is the formation of protein clusters, which are called Lewy bodies. α-Syn (a presynaptic neuron protein), which is the main component of the Lewy body, is inextricably linked to Parkinson's disease, thus causing great interest in the scientific community. Current research indicates that α-Syn assists Lewy bodies through an intermediate soluble oligomeric conformation (called fibrils). These fibrils are deposited in neuronal inclusions and then cause cell death by affecting intracellular targets and synaptic function.
Previous studies have demonstrated that the 71-82 region of α-Syn is responsible for the aggregation of the entire 140 mer protein. But Dr. Mason’s team noted that early-onset Parkinson's disease-associated mutations were found in another fragment of the protein. After most of the mutations were observed, the mutation was found to be at or very close to the 46-53 region, and they chose to detect a 10-mer based on this peptide. Specifically, they created a 209952 member library of 45-54 sequences, of which Includes known mutations, as well as a selection of residue selections as shown in Figure 1. The polypeptide library is then screened using a multiplexed intracellular protein fragment complementation assay (PCA). On this basis, about 200 candidate genes were screened from the library. Subsequently, a competition-based principal component analysis was performed under sequence-selective growth conditions to clarify the difference in growth rates. Competitive principal component analysis obtained one of the most promising sequences from the initially discovered 200 α-Syn binders, which can be determined by sequencing.
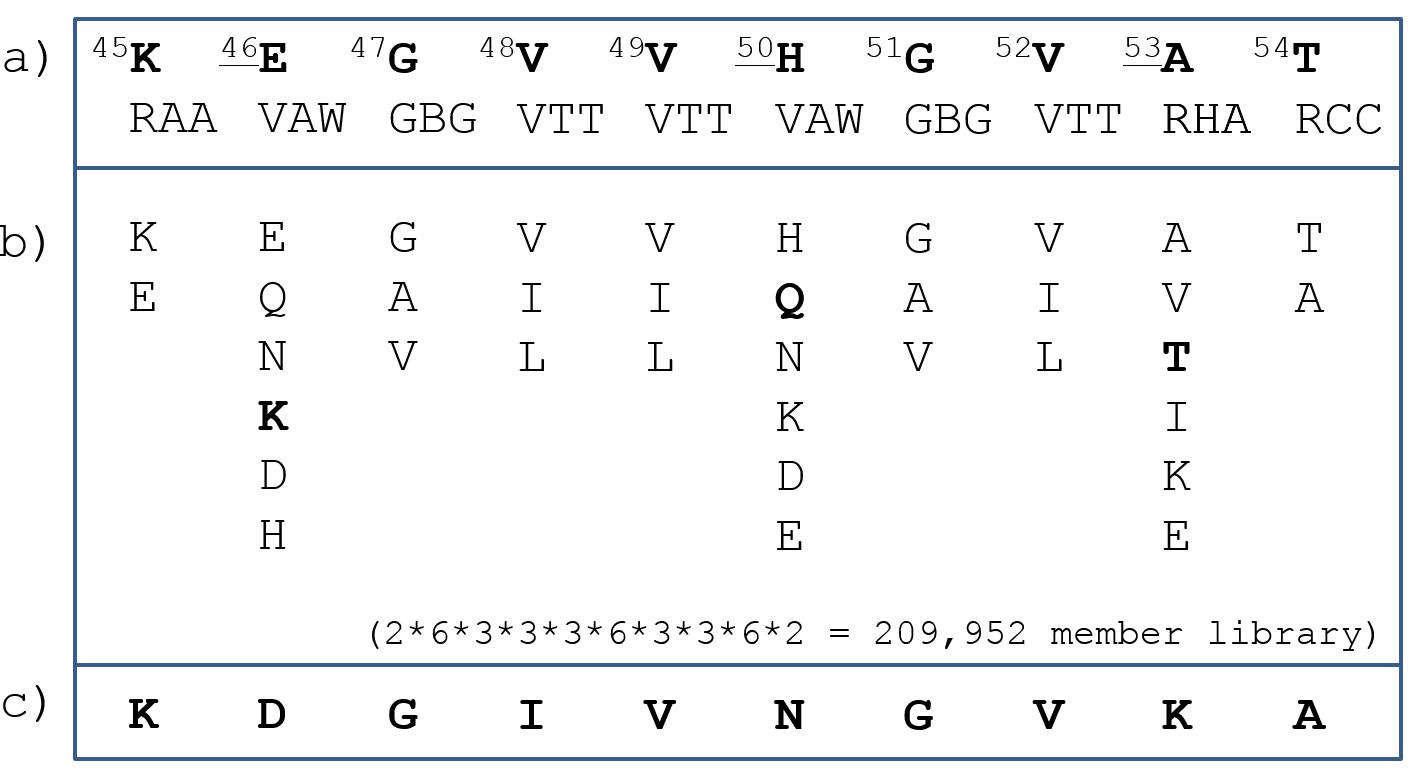 Figure 1.  The 45-54 native sequence of α- S yn (TOP) was used to create a 209952 member peptide library. Including residue positions and options associated with early-onset Parkinson's disease (bold and underlined portion).
Figure 1.  The 45-54 native sequence of α- S yn (TOP) was used to create a 209952 member peptide library. Including residue positions and options associated with early-onset Parkinson's disease (bold and underlined portion).
Lead peptide candidates identified from the competing PCA cycle are able to bind to disease-associated native alpha-Syn and reduce amyloid formation by more than 90%. Then Dr. Mason by solid phase polypeptide synthesis techniques cNOS 45-54, α- S yn peptide (as a control) and the PCA candidates derived peptides to study the effects of 140-mer that native α- S yn-type binding. Peptides derived from the PCA studies can be prevented cNOS α-S yn in 1: aggregation at 1 stoichiometry, the atomic force microscope (FIG. 2), and THT dye binding assay confirmed with circular dichroism experiments confirmed almost completely prevented The beta- sheet secondary structure of the polypeptide . As with the expected selection method, inhibitors also result in a significant reduction in toxicity associated with a-Syn aggregation. Therefore, this study not only validated the method of constructing anti-α- S yn-aggregating peptide inhibitors, but also provided a promising peptide sequence for potential drug candidate molecules.
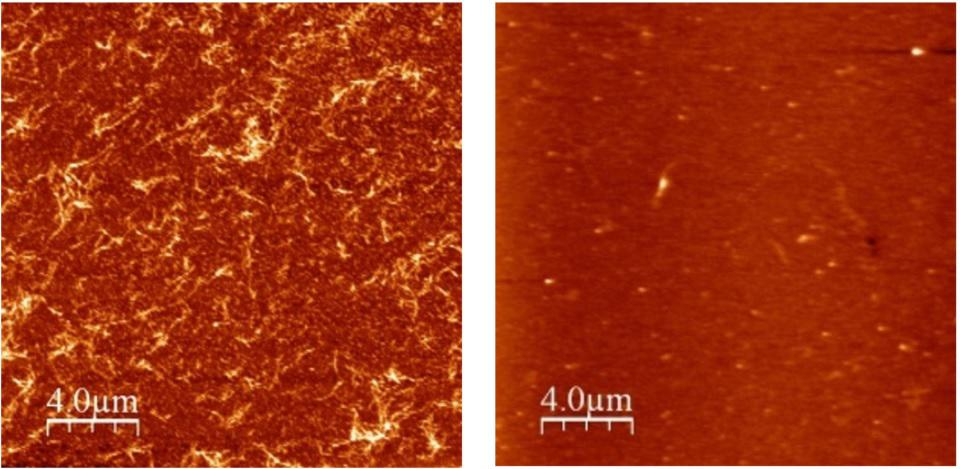
FIG. Left shows the AFM images of the toxic amyloid fibril protein form of α-Syn. These are found in the brains of patients with Parkinson's disease. On the right is the same protein mixed with the newly derived peptide. Binding polypeptide in α- S yn adhesive portion of the protein, almost completely prevents the formation of the fibers.
Dr. Mason started using CEM's Liberty Blue ™ multi-peptide synthesizer at the end of 2013. This system allows him to rapidly synthesize the peptides required for research. Compared to the previous purchase of peptides, it can now save a lot of cost and time, which is very valuable for his work. Another benefit, Dr. Mason no longer cares if there is enough peptide material for experimental problems, because now he can make more peptides quickly and efficiently. Dr. Mason commented: “Since Liberty Blue, we are willing to try more research and face more risk challenges. Liberty Blue is a good complement to our lab and I highly recommend it to other researchers. This system."
Article by Dr. Jody Mason:
Intracellular Screening of a Peptide Library to Derive a Potent Peptide Inhibitor of a-Synuclein Aggregation
Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290 (12), 7426–7435
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.620484
Vaccine For Rabies Prophylaxis
Travelers to areas where rabies is endemic may be at risk, especially if they are likely to come in contact with animals in areas where dog or other animal rabies is enzootic and immediate access to appropriate medical care is unlikely. Canine rabies remains highly endemic in certain areas of the world. Need for rabies preexposure vaccination depends on the nature of risk and associated level of potential exposure. preexposure vaccination based on local incidence of rabies in the country to be visited, availability of appropriate agents for rabies postexposure prophylaxis in that country, and intended activity and duration of stay
Vaccine For Rabies Prophylaxis,Rabies Prophylaxis Vaccine,Freeze Rabies Prophylaxis Vaccine,Freeze Vaccine For Rabies Prophylaxis
Changchun Zhuoyi Biological Co., Ltd , https://www.zhuoyibiological.com