Case Study of Medical Metabolomics: Analysis of Metabolite Information Changes in Asthmatic Patients by Blood Samples by GC-MS
Subject: Human blood
Analytical detection platform: GC-TOF/MS (BIOTREE)
Journal: Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
Impact factor: 2.912
Published time: 2015
Summary:
Aim: To character the specific metabolomics profiles in the sera of Chinese patients with mild persistent asthma and to explore potential metabolic biomarkers.
Methods: Seventeen Chinese patients with mild persistent asthma and age- and sex-matched healthy controls were enrolled. Serum samples were collected, and serum metabolites were analyzed using GC-MS coupled with a series of multivariate statistical analyses.
The results of differential metabolites and several top altered metabolic pathways were identified. The levels of succinate (an intermediate in tricarboxylic acid cycle) and inosine were highly upregulated in the asthmatic patients, Suggesting a greater effort to breathe during exacerbation and hypoxic stress due to asthma. Other differential metabolites, such as 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid and phenylalanine, were also identified. further, the differential metabolites possessed higher values ​​of area under the ROC curve (AUC) Suggesting an excellent clinical ability for the prediction of asthma.
Conclusion: Metabolic activity is significantly altered in the sera of Chinese patients with mild persistent asthma. The data might be helpful for identifying novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for asthma.
Keywords: mild persistent asthma; Chinese patients; serum metabolites; metabolomics; succinate; inosine; GC-MS
First, the research background:
Asthma is often caused by inflammation of the respiratory tract, but there is still a lack of simple and effective measures for rapid determination of respiratory inflammation. Metabolites derived from urine, blood, and exhaled condensate can be used for disease typing and diagnosis. Metabolomics techniques can detect the most important metabolites and metabolism associated with disease by analyzing the metabolite fingerprints of the above samples. way. For these highly specific biomarkers, rapid detection methods can be further established for the classification and early diagnosis of complex diseases such as asthma. This study attempted to analyze blood samples from asthma patients by GC-TOF/MS method to obtain potential biomarkers that may be used for early diagnosis.
Second, the method flow:
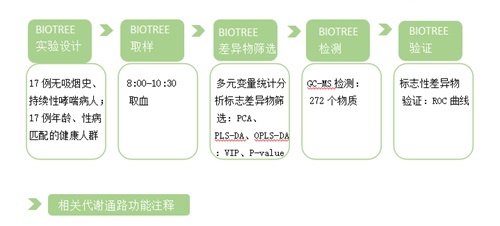
Third, the research results and discussion:
1, the serum metabolome data found significant distinction between the normal and disease:
1) Using GC-MS data to distinguish between patients with mild persistent asthma and healthy people
2) Changes in serum sample metabolomes demonstrate that asthma can cause overall metabolic changes in the human system
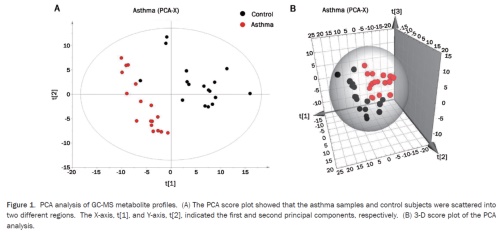
Figure 1 Establishing a PCA model by statistically analyzing GC-MS data with multiple variables
2 , screening to obtain iconic differences: succinic acid, dihydroxybenzoic acid, inosine
1) Difference in succinic acid performance only in the TCA cycle: the condition may be early, without causing global changes;
2) Many metabolites are associated with inflammatory responses, hypoxic stress, etc.;
3) The above substances can be used as biomarkers for early diagnosis of asthma
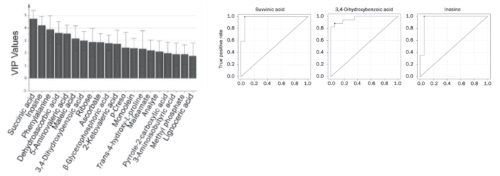
Figure 2 Using VIP to screen for iconic differences, and ROC curves for related substances
3 , the pathogenesis of asthma related metabolic pathways:
1) Routes of influence: TCA cycle, nitrogen metabolism, glutamate metabolism, ribose metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism
2) TCA cycle metabolic enhancement: lack of oxygen leads to strong energy demand
3) Inflammation response
4) Nitrogen metabolism disorder
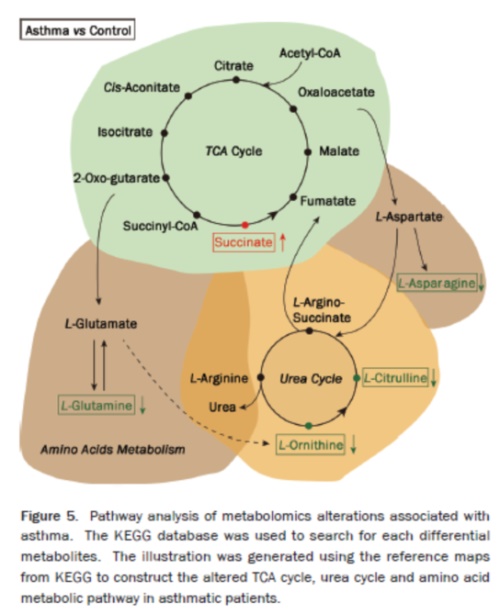
Figure 3 Metabolic pathways that may be involved in the pathogenesis of asthma
Fourth, highlights and prospects:
l found specific metabolite information in the serum of asthma patients;
l Propose possible metabolites for early diagnosis of asthma;
l Identify key metabolic pathways associated with asthma:
A. Increasing cases and further interpretation of metabolite information can help to understand the causes of mild persistent asthma
B. The final identification of biomarkers needs to be proved in the crowd cohort experiment.
Read the literature download address:
Chun CHANG, et al, Investigation of metabolic alterations in asthma by GC-MS based metabolomics analysis. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2015. 36:1356-1366.
Food additives refer to chemical synthetic or natural substances added to food for the purpose of improving the quality, color, aroma and taste of food, as well as for the need of preservative and processing technology. Due to the rapid development of the food industry, food additives have become an important part of the modern food industry, and has become an important driving force of technological progress and technological innovation in the food industry. In the use of food additives, in addition to ensuring their due function and role, the most important thing is to ensure the safety and health of food.
Food And Beverage Additives,Stevia Erythritol Blend,Sweetener Enhancer Nhdc,D-Psicose Sweetener Powder
Xi'an Double H Health Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.dhextract.com