Ding Xiaojun Gu Peiming Zhang Wei Zhou Yue Li Jing
Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd.
Key words: meat adulteration; quantitative analysis
introduction
"Hanging the head, selling dog meat" is a idiom for everyday use. Although with the development of time, this sentence has been difficult to reflect the most real situation, in most parts of the world, dogs have not been used as a source of meat, even in a few places where dog meat is eaten, the price of dog meat is often better than lamb. Still high, has lost the meaning of fraud. However, the fact that such a product mark is inconsistent with the composition of the actual product is a long-term existence. Since the EU's “horse meat storm†in 2013, the phenomenon of adult meat adulteration has also been reported frequently, further deepening people's concerns about the authenticity of meat. This unmarked addition, which greatly disrupts the market order, affects the emotions and health of related religious people, special customs and some meat fasting people, and also brings about potential pathogenicity and disease control problems. The most commonly used methods for detection are: nucleic acid-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on antibody antigen binding. The former suffers from DNA degradation, interference from complex matrices, and sample extraction and amplification methods, interfering with qualitative and quantitative accuracy. The latter is often subject to the preparation of antibodies, protein denaturation during processing, and the effects of false positives caused by homologous interference between complex matrices and close relatives [1, 2].
With the maturity of bio-mass spectrometry, large-scale qualitative and quantitative techniques for studying protein expression profiles have matured. Therefore, the use of mass spectrometry to find and quantify the characteristic proteins or peptides of different meat samples can avoid the above-mentioned problems faced by the most commonly used PCR techniques and ELISAs, including: not affected by the process of food processing, Because the amino acid sequence is easier to preserve than the nucleic acid sequence during processing; at the same time, qualitative and quantitative are achieved, false positives are avoided and the quantitative results are more accurate and reliable; multiple false positives can be monitored simultaneously [2].
Pork, poultry, beef and lamb are the four most consumed meats in the world [3]. In most cases, lamb is the most expensive and may be more than five times more expensive than the cheapest poultry. In real life, it has the greatest adultery temptation for unscrupulous traders. Based on the ultra-high resolution Q Exactive mass spectrometry platform, we studied the characteristic peptides of five common meats. Some of the peptides found were selected, and several different meats were artificially mixed to simulate the adulteration of the reality. A quantitative method of adulteration based on SRM (Selected Reaction Monitoring) was established with TSQ Qμantiva. The entire experimental process is as follows (Figure 1):
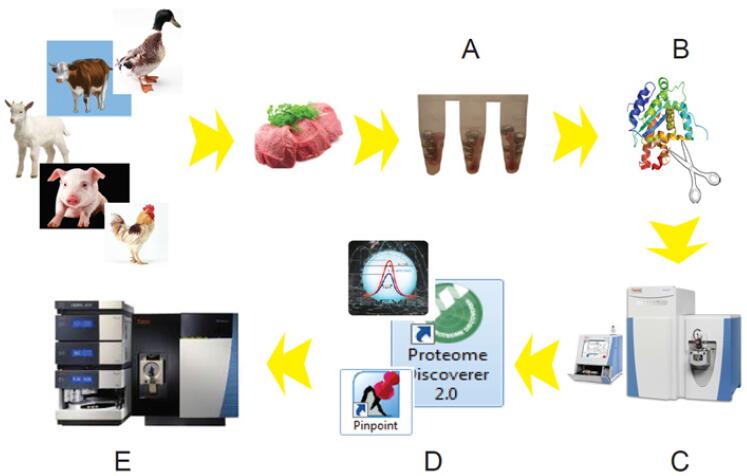
Figure 1. Meat authenticity solution based on the Thermo mass spectrometer platform. (A: sample lysis; B: meat lysate sample reduction alkylation cleavage; C: high resolution mass spectrometry platform for each species data; D: Proteome Discoverer 2.0, SEIVE 2.0 software for species characteristic peptides, Pinpoint software batch generation Quantitative ion pair; E: TSQ Quantiva quantitative analysis)
experimental method:
1. Materials and sample preparation
The meat samples used in this experiment were beef, pork, chicken and duck meat purchased from a large supermarket in Shanghai. The lamb was purchased from a mutton store in Shanghai. Five kinds of meat samples were peeled and fat were taken from pure muscle samples about 100 mg respectively. After cleavage with RIPA lysate, acetone was precipitated. After the urea was dissolved, some of the measured concentrations were taken. The remaining samples were reductively alkylated, and the enzyme was cut overnight, and the solid phase extraction was desalted. It was concentrated by centrifugation, dissolved in 0.1% FA, and used.
2. Adulteration experiment
The chicken and duck lysate were mixed in equal proportions, and 1 μg of the total protease-cut product of the sheep was taken, and the lysed products of chicken and duck were added, respectively, 1 μg, 100 ng, 10 ng, 5 ng, 1 ng, 0.1 ng, Simulate different proportions of adulterated samples and inject three times per sample.
3. Chromatographic conditions
The liquid phase RSLC U3000 has a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min, the mobile phase A phase is 0.1% FA/H 2 O, and the mobile phase B phase is 0.1% FA/ACN. Column Accucore-150-C18, 100mm*2.1mm. The gradient conditions are:
Table 1. Chromatographic gradients
Time (min) | Phase A ( % ) | Phase B ( % ) |
0 | 100 | 0 |
0.2 | 90 | 10 |
16 | 60 | 40 |
17 | 20 | 80 |
17.5 | 20 | 80 |
18.5 | 100 | 0 |
20 | 100 | 0 |
4. Mass spectrometry acquisition method
The mass spectrometry ion source parameters were set to: spray voltage 3500 V, sheath gas 38 Arb, auxiliary gas 15 Arb, backflush gas 0 Arb, ion transport tube temperature 275 ° C, ion source atomization temperature 380 ° C. The mass spectrometry acquisition parameters were: acquisition period of 0.3 s, collision gas of 1.5 mTorr, Q1 and Q3 resolution of 0.7, and source cracking energy of 0.
Experimental result
1. Confirmation of characteristic peptides of species
Species-specific peptide search validation is a key point in meat adulteration experiments, so we studied five common meats through the high-resolution Q Exactive mass spectrometry platform. The peptides specific to each species were selected, and the polypeptides containing the enzyme cleavage sites were removed. The number of polypeptides specific to each species relative to the other four species was identified as: 339 chickens, 125 ducks, and 426 pigs. There are 337 cattle and 152 sheep. Among them, chickens and ducks are avian poultry, sheep, cattle, and pigs are mammalian mammals. The evolutionary relationship between the two is closer. We also found chickens and ducks relative to the other three beasts. There are 336 peptides of class specificity. Pep003 is a characteristic peptide derived from chicken/duck, and Figure 2 is an XC (eXtracted Ion Chromatogram) image of Pep003 quantified by TSQ Quantiva in different adulterated samples:
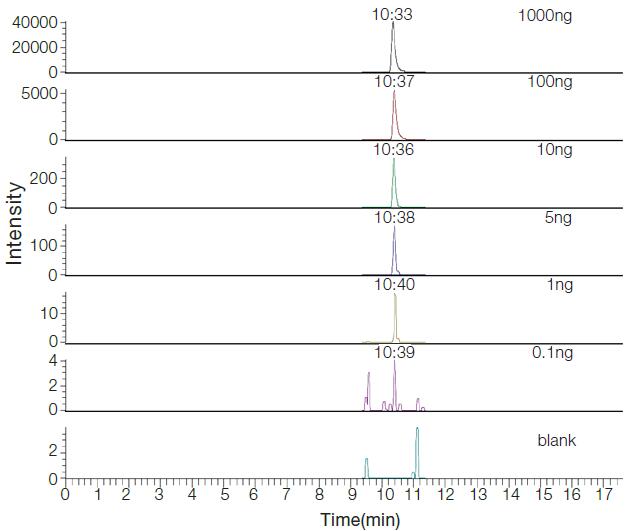
Figure 2. TSQ Quantiva quantifies the XIC plot of Pep003 in samples with different adulterative ratios
2. Quantitative ion pair selection
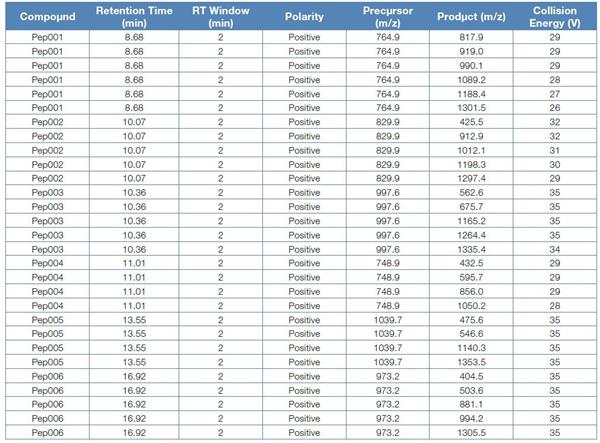
Based on the abundance information, we selected six chicken and duck characteristic peptides (without nicking sites, no methionine, no NXS/T glycosylation motif), imported into Pinpoint software, using Pinpoint The software automatically derives the ion pair and collision energy information, first collects the information of the sample once, uses the Pinpoint software to generate the schedule information, and imports the instrument to automatically generate the final acquisition method. The ion pair information in the method is shown in the following table:
Table 2. Quantitative ion pair and schedule information
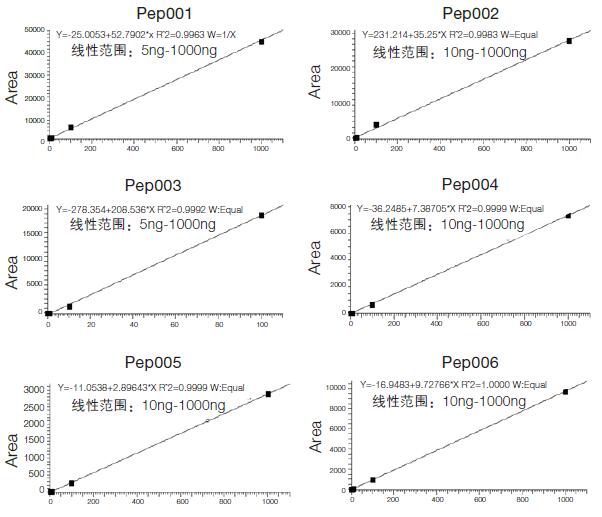
3. Quantitative results and lower limit of quantitation
By adding chicken and duck meat to 1 μg of mutton in different proportions, the SRM method was used to quantitatively study the lowest ratio of the detected ratios, and the above polypeptides were separately quantified using the Xcalibur quantification module to determine the linear range. . Both Pep001 and Pep003 are able to quantify the minimum adulteration of 5 ng, and the remaining four can be quantified to 10 ng adulteration. That is, 0.5% of adulteration and 1% proportional adulteration can be detected respectively. The actual standard curve and linear range are as follows:
Figure 3. Quantitative standard curve and linear range
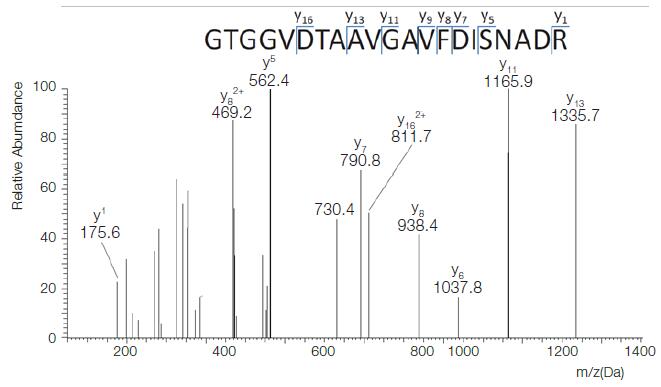
4. Use QED for qualitative confirmation
QED (Qualitative Enhanced Data) scanning function refers to real-time acquisition of signals by monitoring SRM, using secondary particle ion intensity triggering, collecting the full-spectrum spectrum of the corresponding parent ion secondary fragmentation, and obtaining more accurate qualitative information while quantifying. Features. Through QED technology, we collected the QED spectrum of Pep003. Figure 4 shows the actual spectrum of the theoretical polypeptide Pep003 and the theoretical b, y ion matching results:
Figure 4. QED full scan ion map of Pep003
discuss
1. Number of specific polypeptides monitored
In the discovery study, we found only one of the six pig-specific peptides reported in the literature [4-6], and two of them were single amino acid mutations, and the other three were not found; 21 articles reported in the literature Chicken-specific peptides we found 17 [6, 7], one of which reported acetylation modification, and our retrieval process did not add this modification. Modern domestic pigs are domesticated by wild boars. After about 9000 years of long-term domestication and rearing, there are great differences between subspecies and subspecies, and the expression of proteins in different regions or strains of pigs. There are great differences [8]; and single amino acid polymorphism (SAP) is a common phenomenon in nature, and both regional and individual differences can cause this result. Based on the above information, due to the differences in animal genotypes and the effects of sample processing, only one peptide is selected for each species for quantification, which is likely to result in a large area of ​​false negative detection. It is necessary to increase each The number of peptides monitored by each species reduces the probability of false negatives.
2. It is possible to use a polypeptide shared by some closely related species to achieve simultaneous screening.
Chickens and ducks are common carnivorous birds. Relatively close to the other three meats, we do find that the number of specific peptides they share (336) is even larger than the duck we found. The number of specific polypeptides (125). In this way, it is also possible to partially compensate for the imperfect protein database of many species (the duck protein database is not complete). At the same time, chickens and ducks have both common and relatively mammal-specific peptides, which often increase the possibility of sharing with other birds. To some extent, the more economical part realizes the possibility of adding some unknown birds.
in conclusion
Based on Thermo Scientific's comprehensive mass spectrometry solution, we established a complete process from the discovery of adulteration, the selection of quantitative peptides, and the quantitative realization, and conducted adulteration and quantitative capabilities of some of the discovered peptides. Based on the experimental results, for each species, we should monitor as many peptides as possible, and try to avoid false negative results. We also selected six characteristic peptides of chicken and duck, and monitored the adulteration of two kinds of poultry meat, and determined that the minimum adulteration monitoring limit was 0.5%. Considering the economics and operability of the adulteration ratio, it far exceeds the actual monitoring needs.
Compared to traditional PCR-based and antibody-based assays, mass spectrometry has roughly comparable sensitivity, but has better ability to avoid false negative and false positive results, and can avoid PCR or antibody-related processing due to processing. The impact of the destruction of the spatial structure.
Compared with the above adulteration, there is also a relatively serious, more serious adulteration - adulteration of sick meat. Based on the above ideas, we believe that through further systematic research, mass spectrometry can also be a means of monitoring sick and dead meat, cutting off the claws of sick and dead meat flowing into the table, together with our comprehensive pesticide screening and detection methods. Food safety provides a full range of protection. At the same time, using this research method, we can also help organic meat producers to provide the possibility to establish a meat quality selection basis to meat quality standards.
references:
1. Nakyinsige, K., YB Man, and AQ Sazili, Halal authenticity issues in meat and meat products. Meat Sci, 2012. 91(3): p. 207-14.
2.Sentandreu, MA and E. Sentandreu, Peptide biomarkers as a way to determine meat authenticity. Meat Sci, 2011. 89(3): p. 280-5.
3.http://
4. von Bargen, C., et al., New sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of horse and pork in halal beef. J Agric Food Chem, 2013. 61(49): p. 11986 -94.
5. Vargen, Food, MS, B. 62(39): p. 9428-35.
6. Montowska, M., et al., Rapid detection of peptide markers for authentication purposes in raw and cooked meat using ambient liquid extraction surface analysis mass spectrometry. Anal Chem, 2014. 86(20): p. 10257-65.
7. Sentandreu, MA, et al., A proteomic-based approach for detection of chicken in meat mixes. J Proteome Res, 2010. 9(7): p. 3374-83.
8. Ramos-Onsins, SE, et al., Mining the pig genome to investigate the domestication process. Heredity (Edinb), 2014. 113(6): p. 471-84.
One Button Fast Measuring Instrument Vertical
This equipment is widely used in electronic manufacturing, automotive manufacturing, mechanical processing, LCD displays, medical devices, industrial materials, aerospace, precision hardware, green energy, and other small-scale products and components for batch rapid measurement.

Instrument Introduction
1. Ultra large field of view, no distortion, fully automatic, and high-precision.
2. Simply place the workpiece in the effective measurement area and lightly press a button to instantly measure all two-dimensional dimensions.
3. Any workpiece can be placed and multiple measured objects can be recognized simultaneously.
4. Any tedious measurement task becomes incredibly simple.
Instrument functions
1. Automatic matching: For the same product, it only needs to be programmed once and automatically matched during measurement.
2. One click calibration: multi angle, full field of view, ensuring measurement accuracy.
3. Measurement function: any two-dimensional point, highest point, line, highest line, circle (center coordinate, radius, diameter, roundness, perimeter, area, maximum radius, minimum radius), arc, rectangle (center coordinate, length, width, perimeter, area), ellipse (center coordinate, major axis, minor axis, perimeter, area), keyway (center coordinate, length, width, perimeter, area), imported CAD contour scanning comparison, contour PV Area comparison, cylinder diameter, sealing ring (radius calculated through perimeter, maximum radius, minimum radius, thickness of sealing ring), measurement results recalculation (maximum, minimum, average, sum), QR code recognition, barcode recognition.
4. Contour scanning: Quickly scan contours and export DXF files.
5. Easy to use: easy to learn, use, and get started.

One Button Fast Measuring Instrument Vertical,One Button Fast Measuring Instrument,One Button Quick Measuring Instrument 0.5,One Button Quick Measuring Instrument 0.1
Zhejiang dexun instrument technology co., ltd , https://www.dexunmeasuring.com